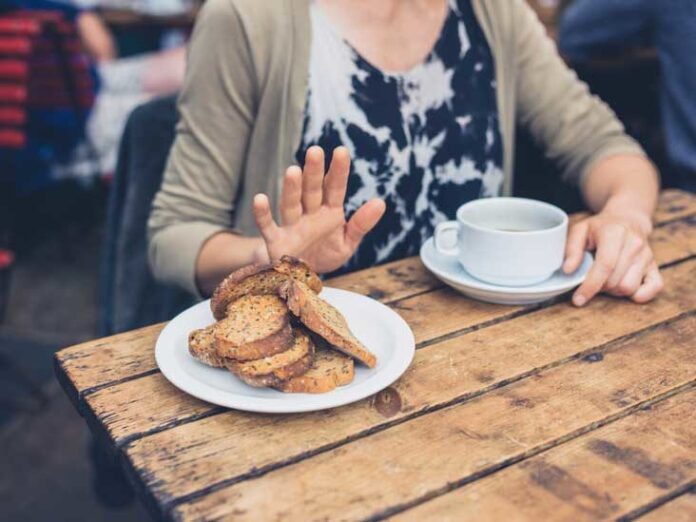
Celiac disease can be described as an autoimmunity issue that occurs when the body attacks the wall of its colon. This inflammation-related reaction can be caused by the consumption of gluten. Gluten consumption triggers an reaction where the body’s systems damage the villi inside the small bowel, and they are destroyed. Villi are the place where nutrients requirements are generally absorbed by the body shortly after processing in the stomach. In time, it’s the poor absorption of the nutrients causes the majority of symptoms or signs that appear in people suffering from Celiac disease. Gluten is an ingredient that can be found in barley, wheat, and rye. Therefore, foods made with these ingredients will definitely cause an inflammation reaction. Celiac disease can be found on one percent of people however, it is more likely to affect more, as the mildest cases aren’t recognized. The reason for this is not clear but there is an elevated risk of inheritance which is why it is thought that an environmental trigger causes the immune system to respond to gluten for those who are genetically susceptible. In certain cases, another immune-related issue, such as Type 1 diabetes mellitus, is also possible. A skin disorder that results in the appearance of a rash on the skin is commonly associated with this condition.
In children of the ages of 5 and under, the typical symptoms of Coeliac disease include loose bowels as well as bloated tummy and stomach pains, wind as well as light stool as well as nausea, bowel obstruction and vomiting. They could vary in intensity. In time, symptoms and signs start to manifest due to lack of absorption of nutrients like an inability to gain weight and anemia, as well as an irritability. In adults , the symptoms are usually looseness of bowels, fatigue and weight loss as well as bloated tummy abdominal pain constipation, anemia nausea, and queasiness. A diagnosis for Celiac disease is made through the use of blood tests to detect those Celiac markers. This type of test isn’t conclusive, but it can be highly informative, especially when the amount of Celiac markers is extremely high. 10 percent of the times the test could result in an inaccurate negative. The most definitive way to determine the diagnosis is performing a biopsy of small bowel using an endoscope. The procedure involves cutting off a small portion of the bowel and is examined using a microscope to determine the distinctive variants of the disorder’s damage. The test is not needed to determine the diagnosis, but it could be utilized as a screening for family members to determine whether they are at a higher risk.
It is not possible to treat Coeliac disease. People who have been diagnosed with it will have to follow a gluten-free diet for the rest of their life. The damage to the intestines will definitely be gradual return to normal after a time and blood tests that show the markers will increase as time goes by. A dietetic consultation with a dietitian immediately after receiving medical diagnoses is essential. Additionally, at the period of the diagnosis, supplements can be given to fix a few absorption problems. A transfusion of iron is often required during this time. The chances for those suffering from Coeliac disease are very good when they adhere to the diet regimen. There is research underway regarding the development of genetically engineered grain that can be used by those suffering from the condition.